Game development is the complex process of turning an idea into an interactive digital experience that entertains and engages players across various platforms. It combines creativity, technology, and strategy to create games for PC, consoles, mobile devices, and emerging platforms such as virtual and augmented reality. It requires careful planning, collaboration among diverse disciplines, including game design, programming, art, animation, sound, and user experience.
The gaming industry is one of the fastest-growing sectors globally. According to market research, the global game development market is expected to grow from approximately USD 1.83 (Source) billion in 2025 to USD 3.45 billion by 2030. Moreover, the overall gaming industry revenue is projected to exceed USD 312 billion by 2025. This rapid growth highlights the increasing demand for innovative, high-quality games and the expanding opportunities for new studios.
This guide aims to provide new developers, indie creators, and aspiring entrepreneurs with a clear roadmap. It covers the essential stages of game development, common challenges, mistakes to avoid, and the increasing role of artificial intelligence in streamlining development processes.
Understanding the Game Development Lifecycle
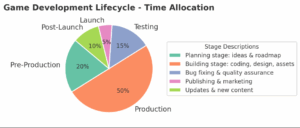
The game development lifecycle is the step-by-step process of transforming a game idea into a fully playable product. It consists of several key phases, each crucial for ensuring the final game meets creative goals and technical standards. These phases include:
Pre-Production: Planning and Validation
Pre-production is the foundation of your game project. During this phase, your team defines the game’s concept, scope, art style, gameplay mechanics, and technology stack. This planning stage typically accounts for about 20% of the total development time.
Market research plays a vital role here. Successful studios analyze player preferences, study competitors, and explore monetization models to validate their game ideas. By the end of pre-production, you should have a clear roadmap and design documents that guide the entire project.
Production: Building the Game
Production is where your ideas take shape. Developers write code, artists create characters and environments, animators bring movement to life, and sound designers compose music and effects. Collaboration and iterative testing are essential to refine gameplay and fix issues as the game evolves.
Efficiency during this phase impacts both the budget and the schedule. Many studios use agile methodologies to adapt quickly to changes and maintain steady progress.
Testing: Quality Assurance
Before launch, rigorous testing is essential to ensure your game performs well across devices and meets quality standards. Testing includes:
- Functional Testing: Identifying bugs in gameplay and mechanics.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the game runs smoothly on different hardware and operating systems.
- Localization Testing: Checking language accuracy and cultural appropriateness for different markets.
- Compliance Testing: Meeting certification standards required by platforms like PlayStation, Xbox, and Nintendo.
Thorough QA minimises post-launch issues and improves player satisfaction.
Launch: Publishing and Marketing
Publishing your game involves submitting it to the chosen platforms, gaining approval, and executing a marketing strategy. Promotion is key to gaining visibility and attracting players, especially for new studios.
Post-Launch Support: Updates and Engagement
Game development doesn’t end at launch. Post-launch support involves fixing bugs, adding new content, and responding to player feedback. This ongoing engagement helps maintain a loyal player base and extends the game’s lifespan.
Core Elements of a Game
Every successful game relies on several fundamental elements that work together to create an immersive experience. Understanding these core components helps new studios design games that are fun, engaging, and memorable.
Game Mechanics
Game mechanics define actions, challenges, and goals, shaping the gameplay experience. In 2025, modern games increasingly use procedural generation, adaptive AI, and physics-based simulations to keep gameplay dynamic and unpredictable.
Arnab et al. (2015) conducted significant research on connecting learning mechanics with game mechanics through what they termed the LM-GM Model. This framework illustrates how game mechanics align with the various “processes and activities” involved in teaching and learning.
Game Design
Game design is the blueprint that outlines how your game functions and flows. It includes level design, player progression, controls, and user interface. A well-planned design aligns gameplay with player expectations, making the experience intuitive and enjoyable.
Research, such as the LM-GM Model (Arnab et al., 2015), highlights the connection between game mechanics and learning processes, demonstrating how games can educate while entertaining.
Visuals
Visuals form the first impression. Characters, environments, lighting, and UI design all contribute to the game’s aesthetic appeal. High-quality graphics not only attract players but also enhance immersion by making the world feel believable.
Sound and Music
Sound effects and music are essential for setting the mood and atmosphere. They bring life to actions, evoke emotions, and provide feedback to players. Well-crafted audio can transform a good game into a memorable one.
Story and Characters
Compelling stories and well-developed characters give your game emotional depth and purpose. They help players connect with the game on a personal level, increasing engagement and retention.
User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI)
UX and UI design dictate how players navigate your game and interact with its features. A clean, organised interface improves accessibility and keeps players focused on gameplay rather than struggling with controls. Poor UI design is a common game development mistake that can drive players away.
Common Game Development Challenges Every New Studio Faces
Building a game is an exciting journey, but it comes with its fair share of hurdles. New studios and newbie game programmers often encounter technical and creative challenges that can slow down or even halt progress. Understanding these common obstacles helps you prepare and avoid costly mistakes.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Designing your game to run smoothly on multiple platforms like PC, consoles, mobile devices, and emerging platforms like VR and AR is a complex task. Each platform has unique hardware specs, screen sizes, and performance limits. Ensuring your game looks good and performs well across all devices requires careful optimization and testing. Failure to do so can lead to poor user experience and lost players.
Real-Time Performance Optimization
Games must run seamlessly in real-time to keep players engaged. Lag, crashes, and slow load times frustrate users and can lead to negative reviews or abandonment. Performance optimization involves fine-tuning code, managing resources efficiently, and using tools to monitor frame rates and memory usage.
Security and Anti-Cheat Systems
Protecting your game’s code and data from hackers and cheaters is essential, especially in multiplayer games. Security measures like encryption, secure servers, and cheat detection systems safeguard both your intellectual property and the fairness of gameplay.
Time Management
Many studios struggle with time management by adding too many features or expanding the project beyond the original plan. This leads to missed deadlines, budget overruns, and burnout. Effective project management, clear milestones, and sticking to a realistic game development lifecycle are key to success.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Comprehensive testing is vital to identify bugs, glitches, and compatibility issues before launch. Specialized QA includes functional testing, compatibility testing, localization checks, and compliance with platform standards. Neglecting QA can result in costly fixes after release and damage to your studio’s reputation.
Popular Game Engines And Tools Used For Game Development
There are many popular game engines and tools on the market. You should use top-quality premium tools for making high-quality games. The top 10 most popular game engines and tools are listed below.
- Maya
It is used for making 3D characters, environments, and animations in games.
- Godot Engine
Free, open-source engine for both 2D and 3D games. Great for indie developers.
- Unity
Popular engine for mobile, console, PC, and VR games. It is known for its versatility and huge asset store.
- O3DE
It is an open-source engine for realistic 3D worlds and simulations. It is ideal for large-scale projects.
- Gamefroot
It is a web-based tool for simple games. It is often used by educators to teach game design.
- GDevelop
This tool enables you to make 2D games without coding, making it good for fast ideas and new learners.
- GameMaker
It is one of the most popular tools for making 2D games.
- Construct 3
It is a browser-based 2D game creator, making it great for puzzle and arcade-style games.
- Unreal Engine
It is a high-end tool for AAA games. It is used to make very realistic graphics.
- PixiJS
It is a JavaScript tool for 2D games which works in browsers. It works well for all web apps.
Future of Game Development With Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is changing the face of game development. It’s now helping developers automate testing, generate realistic characters, and create dynamic environments. AI tools make game development more efficient, even with limited resources. AAA games usually need 3 to 4 years to go from idea to testing. Now, AI is making many of these steps much faster.
AI integration with neural rendering, haptic feedback, and mixed reality could blur the line between virtual and real-world play. Game worlds will adapt to individual player styles, emotional states, and even biometric data, making experiences more immersive than ever.
Conclusion
In short, game development is a complete process of designing and building games from scratch. The game concept is transformed into a playable reality. There are many challenges that can be faced in this process. But these can be reduced by following the right techniques. Artificial Intelligence is also playing an essential role in every field, like game development. Making this process faster and easier.
Game development is a complex, multi-stage process that transforms creative ideas into interactive digital experiences. From pre-production planning and production to rigorous testing and post-launch support, every phase demands careful attention to detail and technical expertise.
FAQ’s
Which game engine should I choose as a beginner?
Beginner-friendly engines like Unity, Godot, and GDevelop are great starting points. They offer extensive tutorials, community support, and easy-to-use interfaces.
How do I test my game before release?
Share early builds with friends or use online beta testing platforms to gather feedback. Automated AI-based testing tools can also help detect bugs and performance issues efficiently.
What do I need to start a game studio?
You need a clear game concept, essential development tools, and a small team skilled in design, programming, and art. Proper planning and market research are also vital.
What are common game development mistakes new studios make?
Typical errors include starting without a clear plan, ignoring the target audience, overcomplicating gameplay early on, poor UI design, and insufficient testing.
What’s the difference between an indie developer and a game studio?
Indie developers are usually small, self-funded teams with creative freedom but limited budgets. Studios tend to be larger, investor-backed, and manage bigger projects with tighter schedules.
Should I start with mobile game development or PC game development?
Mobile game development is usually faster and more affordable, making it ideal for startups with limited budgets. PC development suits games requiring high-end graphics and complex mechanics.



